Profile: AGRIFORVALOR project – The case of the Andalusian Biomass Innovation Design Hub
Type of post: PROJECT PROFILE.
The AGRIFORVALOR project is just about to end.
This interesting European initiative has brought together members from all sectors
adjacent to the bioeconomy, helping identify where value can be found in
sidestream products from agriculture and forestry. Let us know more about the project
and the specific activities developed in one of its pilot hubs (Andalusia).
Figure 1. Logo of the AGRIFORVALOR Project
Project approach
1. Agriforest wastes ¿problem or opportunity?
Agricultural and forest sectors
generate large quantities of by-products. Usually, they are considered as
wastes and, even, suppose an environmental issue. However, it is better to
think of these materials as an opportunity. The sidestreams from many
agricultural and forestry industry activities have the potential of becoming
valuable feedstock for a range of sectors.
2. There are obstacles limiting the
exploitation of sidestream biomass resources
The main barriers are: the lack of
internal financing; obstacles that originate in legislation and legal
requirements, as well as lengthy administrative and approval procedures; lack
of appropriate external funding sources and uncertainty around economic
viability of the biobased products.
3. AGRIFORVALOR goal
The project was designed to overcome
those obstacles and act as a mediator and facilitator of new commercial
opportunities for the agriculture and forestry sectors. Specifically, the
project aims to bridge the research and innovation divide by connecting
practitioners from agriculture and forestry to research and academia as well as
with associations and clusters, bioindustry, policy makers, business support
organisations, innovation agencies and technology transfer intermediaries in
multi-actor innovation partnership networks.
4. Innovation Design Hubs
The networks
are managed by three Biomass Innovation Design Hubs: Andalusia, South-East
Hungary and Ireland. In each of these hubs, existing research results and good
practices on valorisation of biomass sidestreams from agro and forest are
shared and matched with the specific needs and potentials. The focus is being
placed on regional development.
Key data
Main
objective
|
Identification of potential
biomaterials that were formerly not considered valuable and the development
of the technology needed to exploit them.
|
Call and
topic
|
-
H2020-ISIB-2015-1.
- Funding
scheme: CSA - Coordination and support action.
- ISIB-02-2015 - Closing the research and
innovation divide: the crucial role of innovation support services and
knowledge exchange.
|
Duration
|
From
01/03/2016 to 31/08/2018.
|
Total
cost
(EU
contribution)
|
1.997.416,25
€ (1.997.416,25 €)
|
Project
leader
|
Steinbeis 2i GmbH (Germany)
|
Consortium
|
- Agencia Andaluza del
Conocimiento (Spain)
- Agriculture and food development authority
(Ireland)
- Agrifood cooperatives of Andalusia (Spain)
- Association of Enterprises of Forest and
Landscape in Andalusia (Spain)
- Bay Zoltan Nonprofit Ltd. for Applied
Research (Hungary)
- Gabinete de Iniciativas
Europeas (Spain)
- GrowAbric (Belgium)
- Institute of Technology Tralee (Ireland)
- Irish Farmers Association (Ireland)
- Irish Business and Enterprise Confederation
(Ireland)
- National Agricultural Research and
Innovation Centre (Hungary)
- LAVINA Foundation for agricultural
innovation (Hungary)
- PILZE - Nagy Kft. (Hungary)
- University of Ghent (Belgium)
- Wageningen University & Research,
Environmental Research (Netherlands)
|
Impacts
- In each hub, Steering Committees, consisting
of experts on exploitation and business development, monitored and consulted
the conceptualization and implementation of the trainings and support measures.
-
Tailor-made innovation support tools and materials were developed in line with
the identified needs of forestry and agriculture. The main example is an
interactive online tool on sidestream
biomass that acts as a networking and marketing platform in order to connect
players (winner of the CommBeBiz Innovation Award 2017 as “Best Innovation
Tool”).
- Project
results and experiences were translated into recommendations for a more
demand-driven research agenda as well as long-term end-user materials to feed
into the EIP-AGRI.
The Andalusian Hub
Those are some examples of the
actions and activities carried out in the Andalusian hub:
Business case identification
Opportunities for biomass
valorisation for the large volumes of olive sidetreams generated in this
Spanish region:
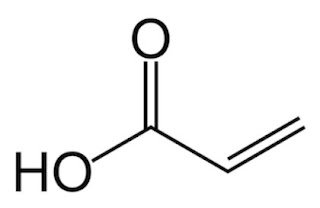
- Extraction of valuable compounds
from the olive mill sidestreams (e.g. polyphenols, anti-oxidants) for
ingredients for food, cosmetics and pharmaceuticals.
- After extraction of valuable
compounds, anaerobic codigestion (mix with pig or cow slurry and other crop
residues) can be applied to produce biogas. The biogas can be sold for heating
purposes (transport through piping) or can be used to generate electricity.
- Techniques using fermentation of
olive mile sidestreams to produce biopolymers, enzymes and biofuels are
promising but have to be further developed and economically validated.
Project consultancy
One of the projects that has
received technical advice and guidance from the Hub is about the use of
composting and vermicomposting of the olive mill effluents and the wastes of
the olive pruning to obtain a high quality and affordable organic fertiliser. The
partnership consists of: Cooperativa olivarera San Isidro de Loja, Universidad
de Granada, Estación Experimental del Zaidín, Cooperativas Agroalimentarias de
Andalucía, Consejo Andaluz de Ingenieros Técnicos Agrícolas. It resulted in an Operational Group funded by
EIP-AGRI and received the Best Business Model Award 2018 in the Andalusian Hub.
Interhub mission
30 experts and professionals of the
sector attended to this meeting that gave them the chance of knowing about
successful business cases of Andalusian companies focused on the valorisation
of agroforest biomass and collaborating in the creation of international
cooperation nets:
- Visit to the biogas plant of GIESA
Agroenergía in Campillos (Málaga). It processes pig slurries mixed with olive
oil processing industry wastes.
- Visit to the plant of the joint
venture NATAC and Oleica El Tejar in Palenciana (Córdoba) where bioactive
compounds are extracted from biomass of the olive grove.
- Visit to the biomass plant of Valoriza
Energía en Puente Genil (Córdoba).
- Visit to the biomass plant of Ence
in Huelva.
- Visit to the pilot plant of the Instituto
de La Grasa in Sevilla, focused on the treatment and valorisation of wastewater
from agrifood industries and other industrial effluent through anaerobic
digestion processes.
Figure 2. Interhub mission: Visit to
the biomass plant of Ence in Huelva (courtesy of AGRIFORVALOR)
Events
- I Workshop AGRIFORVALOR: Valorisation
of agriforest wastes and byproducts in Andalusia (Seville, 24/11/2016)
- II Workshop AGRIFORVALOR: Valorisation
of agriforest wastes and byproducts in Andalusia (Malaga, 15/02/2017)
- Workshop of regulation in the
field of agriforest biomass (Seville, 30/10/2017)
- Workshop AGRIFORVALOR on
opportunities of funding for biomass valorisation (Seville, 16/11/2017)
- I Forum of the Andalusian
Bioeconomy Strategy (Seville, 12/012/2017).
Acknowledgements: I would like to
express my appreciation to Cristina Cabeza (Coordinator of the Andalusian Hub)
for her kind collaboration.