Comet Biorefining raises equity to build its commercial plant for 2G dextrose in Sarnia
Comet
Biorefining announced yesterday the completion of a round of equity
financing led by PM Equity Partner
and with the participation of Sofinnova
Partners and Bioindustrial Innovation
Canada (BIC). Details of the financing were not disclosed but it is known
that the investment will be used to advance the commercialization of Comet’s 2G
sugar production platform and fund the construction of a dextrose facility in
Sarnia (Ontario, Canada).
As background, it should be remembered that Comet
Biorefining:
- informed of the construction of a 60 million
pounds (22,400 ton) per year commercial plant to come online in 2018 producing
sugar from locally sourced corn stover and wheat straw (February 2016).
- was awarded with a grant of CA$10.9 million
from the Sustainable Development Technology Canada (SDTC) for the construction of the
plant (March 2016).
- entered into a memorandum of understanding
with Cellulosic Sugar Producers Cooperative
to collaborate on the development of a sustainable agricultural biomass supply
chain in southwestern Ontario (March 2016).
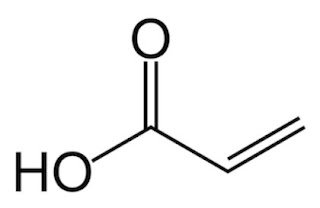
- signed an off-take agreement with biosuccinic
acid producer BioAmber for high-purity dextrose from the planned plant (April
2016).
Figure 1. Aerial view of the Bluewater Energy
Park (extracted from www.bluewaterenergypark.ca).
It is owned by TransAlta and will host the 2G sugar plant of Comet.
The industrial technology of Comet converts
agricultural residues into high-purity dextrose for production of sustainable chemicals.
Comet cellulosic sugar is competitive in terms of cost and quality with corn or
sugarcane derived products, it does not hamper food production and it contributes
to lower carbon economy, improving the sustainability profile of the produced
biochemical. This technology allows biofuels and bioproducts manufacturers to
have a reliable and consistent source of cellulose-based glucose that can be
directly converted to value-added end products. The Comet cellulosic sugar
process uses two stages to activate cellulosic biomass, followed by conversion
to glucose at very low enzyme loading. Co-products are used for energy
production or other applications.