FIRST2RUN Project – From cardoon to biobased products
FIRST2RUN is the name of one of the three demonstration projects that won funding from the BBI JU
2014 call. Since the project is aimed at demonstrating an integrated
biorefinery, the blog will be following its advances with interest. The first data
of the proposal were compiled in a previous post which summarized the
information available in CORDIS about the projects granted in the call (BBI
JU 2014 call – Granted Projects). Novamont (coordinator) has just unveiled
the official web page of the project. It
is for that reason that now, we can deepen a little bit more in the scope and objectives
of the project.
FIRST2RUN will
demonstrate (TRL8: system complete and qualified) the techno, economic and
environmental sustainability at industrial scale of a value chain where underutilized
oil crops are exploited for the extraction of vegetable oils to be further
converted through chemical and biotechnological processes into biomonomers and esters that will be applied in the
formulation of bioproducts.
The cardoon will
be the oil crop to be studied. The demonstration of the agricultural and
industrial sustainability of its large scale cultivation in identified marginal
lands will be carried out in the first stage of the project. Taking this
feedstock as reference, sustainable, cost-effective and innovative catalytic
and biocatalytic processes for the production of biobased building blocks from
high oleic oils (mainly, pelargonic and azelaic acids) will be developed and optimized
at medium scale. Then, the system will be scaled in order to reach a large
scale production of building blocks (20,000 ton/year), biodegradable oils
(10,000 ton/year) and compounded biopolyesters (50,000 ton/year). The formulation
of the biobased building blocks will be validated thanks to their transformation
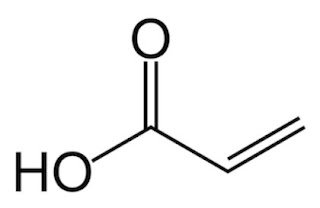
into biobased products. Azelaic acid is a basic constituent of renewable and/or
compostable plastics, in addition to having important applications in the
synthesis of complex esters used in the lubricants sector. Pelargonic acid is
used as an intermediate in the synthesis of biolubricants and emollients for
the cosmetics sector, but it is also an important raw material for the production
of bleaching agents, food fragrances and herbicides.
Figure 1. Azelaic
acid and pelargonic acid (extracted from Matrìca web page)
By and co-products
from the process will be valorised for energy, feed for animals and added value
chemicals in order to increase the sustainability of the value chain. The
side-streams compounds that can be recovered and exploited include
lignocellulosic residues deriving from the cardoon crop, by-products from the
extraction process of oils from seeds, as well as the glycerol produced during
the oxidative cleavage of the high oleic oil.
The project
started on 7th July and it will have a duration of 48 months. The
consortium is formed by six partners from four different countries:
- Novamont SpA (Italy): coordination and demonstration activities.
- Matrica (Italy): demonstration activities.
- Soliqz BV (The Netherlands): products recovery.
- SIP Limited (United Kingdom): formulation and validation of biobased lubricant.
- Biophil Central Europe SRO (Slovakia): formulation and validation of biobased cosmetics.
- Alma Mater Studiorum – Università di Bologna (Italy): development of catalysts.