Chempolis and NRL to build advanced biorefinery in India
Recent news about a cellulosic
ethanol project are coming from India. The Finish Chempolis announced
on 14th February the formation of a Joint Venture with Numaligarh Refinery Limited (NRL) to build a
world class biorefinery using formicobio™
technology in North East India (Assam). The project, representing an investment
of around 110 M€, has already approved from NRL’s board.
The final formalization of the JV
was preceded by several preparation stages including a first Partnership
Agreement between Chempolis and NRL (October
15, 2014) and MoUs with neighboring states of Assam for the sustainable
supply of the raw materials.
Table 1. Technical details of the
project
|
|
Feedstocks
|
Bamboo growing in North-East India.
It may also use other locally
available biomasses such as grasses, sugarcane bagasse and cereals straw.
It will consume annually 300,000
tons of cellulosic biomasses (dry basis).
|
Products
|
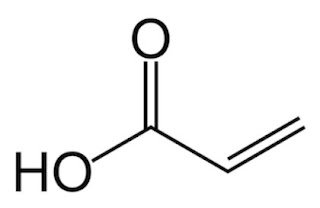
Cellulosic ethanol (48,900 MT/y), platform
chemicals (acetic acid and furfural) and combustible residues (biocoal and lignin).
|
Technology
|
Formicobio™ is a technology for
the production of cellulosic sugars and further ethanol. It has been
specially developed for non-food raw materials (e.g. bamboo, bagasse, straws and
other agricultural residues) and it is based on selective fractionation of
biomass with fully recoverable biosolvent containing formic acid.
The technology enables
co-production of platform chemicals, such as acetic acid and furfural. In
addition, combustion of co-produced solid biofuel (biocoal) can generate all
the energy needed in the biorefinery, with some surplus to be used in other
applications.
|
Figure 1. Simplified flow process diagram of formicobioTM
technology (extracted from “formicobio™
– The future is non-food cellulosic ethanol”)