Delfzijl Biomethanol Plant
Nombre / Name
|
Delfzijl Biomethanol Plant
|
Empresa / Company
|
BioMCN (www.biomcn.eu)
|
Localización / Location
|
Delfzijl (Netherlands)
|
Categoría / Category
|
Comercial / Commercial
|
Estado / Status
|
Operación / Running
|
Plataformas / Platforms
|
Gas de
síntesis / Syngas
|
Materia prima / Feedstock
|
Glicerina / Glycerin
|
Producto / Product
|
Biometanol
/ Biomethanol
|
Puesta en marcha / Start-Up
|
2009
|
Figure 1. Delfzijl Biomethanol Plant
(extracted from Reference 2)
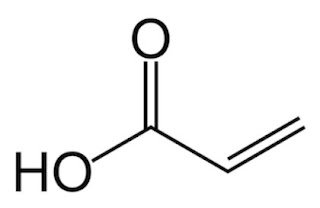
En el año 2006, BioMCN compró una planta convencional de metanol en Delfzijl
(Norte de Holanda). El método tradicional de producción de metanol pasa por el
empleo de gas natural. BioMCN había desarrollado un proceso patentado para
obtener biometanol a partir de glicerina cruda, un subproducto renovable de la
síntesis del biodiesel. La viabilidad del proceso se demostró en una planta
piloto a escala en marzo del 2008, después de lo que se inició la construcción
de una planta comercial de 200.000 toneladas al año que fue puesta en marcha en
el año 2009. In
2006, BioMCN acquired a conventional methanol plant in Delfzijl in the north of
the Netherlands. The traditional method for producing methanol involves the use
of non-renewable natural gas. BioMCN had developed an innovative patented
process that converted crude glycerine into biomethanol, a renewable byproduct
of biodiesel synthesis. The feasibility of the glycerine-to-methanol process
was demonstrated on a pilot plant scale in March 2008, after which the
construction of the 200,000 tonnes per year unit was started. The plant is in
full commercial production since 2009.
Figure 2. Biomethanol production
process diagram (extracted from Reference 2)
La glicerina y el biodiesel se generan a partir de una mezcla de metanol y
aceites y grasas vegetales. En la instalación, BioMCN toma la glicerina y la
transforma en metanol. La glicerina reciclada cierra el ciclo de producción ya
que el metanol obtenido a partir de ella puede ser utilizado luego en la
producción de biodiesel. Desde las plantas de biodiesel, la glicerina cruda es
transportada en barco, tren o camión hasta la planta de BioMCN, donde es
almacenada en tanques. Posteriormente, se purifica, se evapora y se craquea
para obtener el gas de síntesis que se usa en el proceso de obtención del biometanol. Una
vez generado, el biometanol se purifica por destilación y se almancena. From a feedstock mix of
methanol and vegetable oils and fats, the compounds biodiesel and glycerin are
produced. BioMCN takes that glycerin by-product and converts it into methanol.
This glycerin recycling closes the production cycle, because the methanol
produced from glycerin can then again be used in the production of biodiesel. The
crude glycerine from biodiesel plants is transported by ship, train or truck to
the BioMCN plant, where it is stored in tanks. It is then purified, evaporated
and cracked to obtain syngas (synthesis gas), which is used to synthesise the
bio-methanol. Next, the bio-methanol is purified by distillation and is stored.
_________________________________________________________________________________
REFERENCIAS / REFERENCES
2 R.
Blokland: “Bio-methanol by BioMCN”. Innovative uses of glycerol from the
biodiesel process, Brussels, December 13th, 2011
3 IEA
Bioenergy Task 42 Biorefining. Sustainable and synergetic processing of biomass
into marketable food & feed ingredients, products (chemicals, materials)
and energy (fuels, power, heat).
Wageningen, the Netherlands, August 2014.
4
IEA Bioenergy Task 42 Biorefining. Country report Netherlands. November 2014.